Introduction
Prothrombin Fragment 1+2 [F1+2] is an activation peptide that is generated when Prothrombin [Factor II] is converted to Thrombin. Prothrombin is activated to Thrombin [Factor IIa] by a membrane-bound enzyme complex - Prothrombinase and which is assembled through reversible interactions between Factor Xa and Factor Va on membranes containing Phosphatidylserine – a Phospholipid.
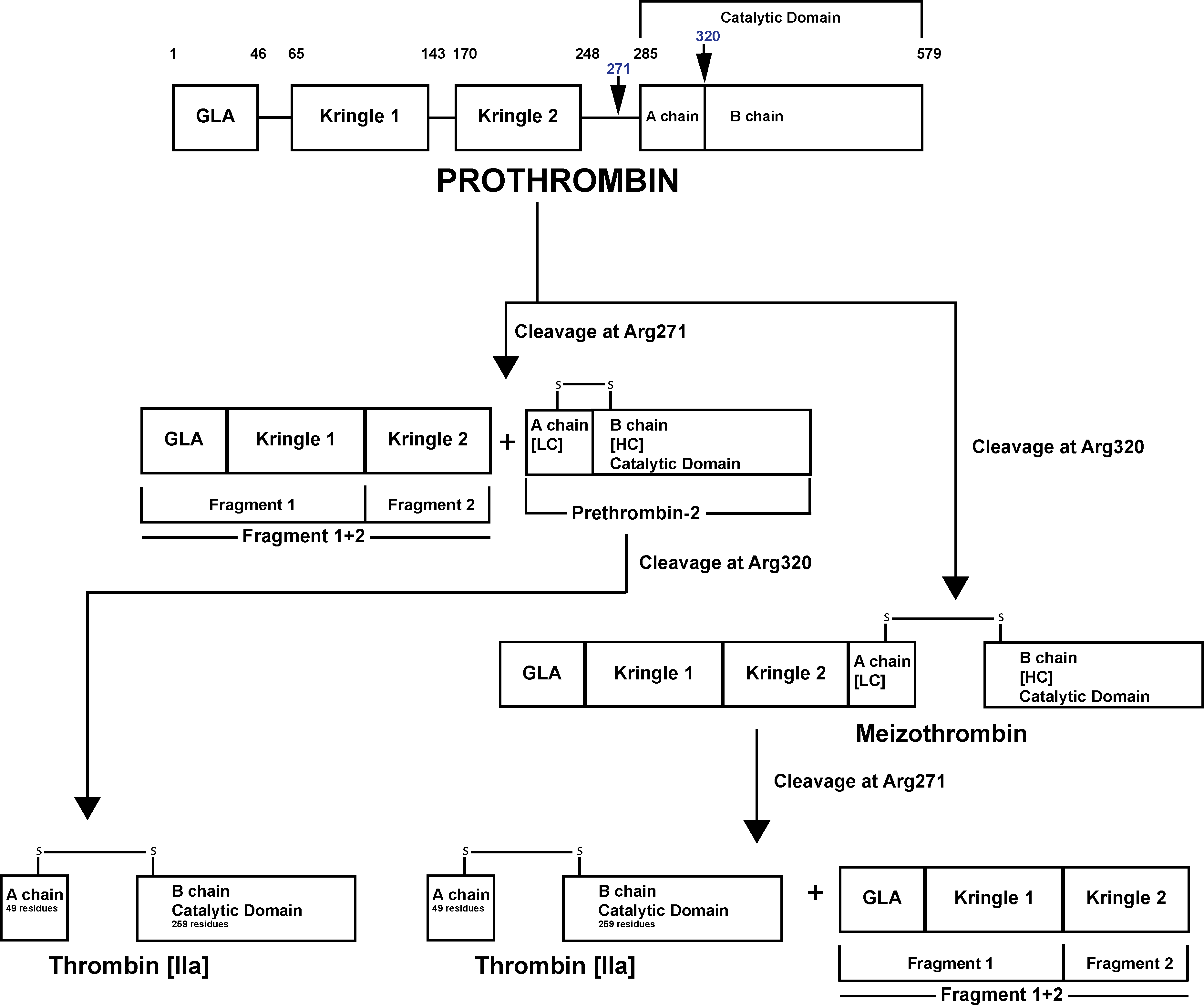
The Prothrombinase enzyme complex cleaves Prothrombin at two sites: Arg271-Thr272 and Arg320-Ile321 resulting in two pathways of Prothrombin activation and possible generation of Prothrombin F1+2:
1. Cleavage at Arg271-Thr272 This generates Prothrombin Fragment 1+2 [F1+2] and the zymogen Prethrombin 2 [PT2]. Subsequent cleavage of PT2 by FXa at Arg320-Ile321 generates a two-chain active Thrombin molecule comprising a 49 residue A chain [the light chain] and a 259 residue B chain [the heavy chain] linked by a single disulphide bond.
This two chain molecule then undergoes further processing by Thrombin which cleaves the A chain at Arg284-Thr285 resulting in a 36 residue A chain and the generation of α–Thrombin.
2. Cleavage at Arg320-Ile321 generates Meizothrombin [mIIa]. Subsequent cleavage of Meizothrombin by FXa at Arg271-Thr272, generates Thrombin and F1+2.
This two chain molecule then undergoes further processing by Thrombin which cleaves the A chain at Arg284-Thr285 resulting in a 36 residue A chain and the generation of α–Thrombin
Prothrombin [Factor II] is activated to Thrombin [Factor IIa] by a membrane-bound enzyme complex - Prothrombinase and which is assembled through reversible interactions between Factor Xa and Factor Va on membranes containing Phosphatidylserine – a Phospholipid.
The Prothrombinase enzyme complex cleaves Prothrombin at two sites: Arg271-Thr272 and Arg320-Ile321 resulting in two pathways of Prothrombin activation:
1. Cleavage at Arg271-Thr272 generates Prothrombin Fragment 1+2 [F1+2] and the zymogen Prethrombin 2 [PT2]. Subsequent cleavage of PT2 by FXa at Arg320-Ile321 generates a two-chain active Thrombin molecule comprising a 49 residue A chain [the light chain] and a 259 residue B chain [the heavy chain] linked by a single disulphide bond.
This two chain molecule then undergoes further processing by Thrombin which cleaves the A chain at Arg284-Thr285 resulting in a 36 residue A chain and the generation of α–Thrombin.
2. Cleavage at Arg320-Ile321 generates Meizothrombin [mIIa]. Subsequent cleavage of Meizothrombin by FXa at Arg271-Thr272, generates Thrombin and F1+2.
This two chain molecule then undergoes further processing by Thrombin which cleaves the A chain at Arg284-Thr285 resulting in a 36 residue A chain and the generation of α–Thrombin.
Prothrombin Fragment 1+2 [F1+2] is stable degradation product and its measurement in plasma can be used as a marker of Thrombin generation. Measurement of F1+2 has been used to diagnose Pre-thrombotic states and Thrombotic disorders and in addition to monitor the efficacy of treatment in these disorders.
F 1+2 has a half-life of about 1 hour and is cleared from the blood by the liver.
Principles
Assays for Prothrombin F1+2 are commonly ELISA-based assays.
1. An antibody specific for the F1+2 fragment is pre-coated onto a micro-titre plate.
2. Standards and patient samples are pipetted into the wells of the micro-titre plate and the plate is then incubated at 37°C. Any F1+2 fragments present in the samples are bound by the immobilized antibody.
3. The wells are aspirated and a Biotin-conjugated antibody specific for the F1+2 fragment is added to the wells.
4. The plate is washed to remove any unbound reagent and
avidin-conjugated Horseradish Peroxidase (HRP) is added to the wells.
5. The plate is washed again to remove any unbound avidin-enzyme reagent and a substrate for the HRP is added to the wells. The resulting colour change is proportional to the F1+2 fragment concentration bound by the immobilised antibody in Step 1.
6.
The colour development is stopped and the intensity of the colour change is derived by measuring its absorbance at 450nm. A standard curve is created using standards of known F1+2 concentration and from which the concentration of F1+2 in the unknown samples can be derived. If the samples have been diluted then a correction is made for this.
